Internal Network Exposure via UPnP NAT Injection

Principal Security Architect
December 5, 2018
Universal Plug-n-Play – (UPnP) is a suite of protocols that enables a device to discover other devices on a network, configure itself to operate in the network, and advertise its services. This allows a device to locate routers, printers and other resources on a network. UPnP runs on UDP port 1900 and communicates using SOAP messages over HTTP. The actual configuration and management interface are implemented using a SOAP-based HTTP service running over a dynamically allocated TCP port. The UPnP protocol allows management of aspects of a device’s operation to extend support by the protocol implementation on the device and its configuration. An attacker can utilize this functionality to control the behavior of devices, like routers that sit at the boundary of a network, and regulate the flow of traffic between the networks.
A device locates other UPnP capable devices on the network by sending a Simple Service Discovery Protocol (SSDP) message as shown in Figure 1. This is the SSDP M-SEARCH message which is sent to the multicast address 239.255.255.250 on UDP port 1900.
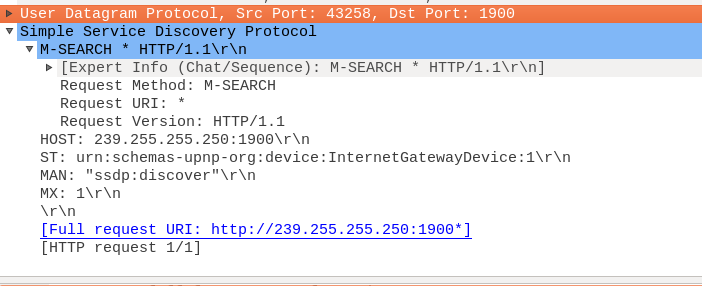 Figure 1: SSDP M-SEARCH multicast message
Figure 1: SSDP M-SEARCH multicast message
A UPnP capable device will respond with a unicast SSDP message as shown in Figure 2. The response message, among other things, will inform the querying device of the URI on the UPnP device, which can be queried for further information. The “LOCATION” parameter in the response can be queried to gather device information, like the software type, software version, URL’s of the control interface, etc.

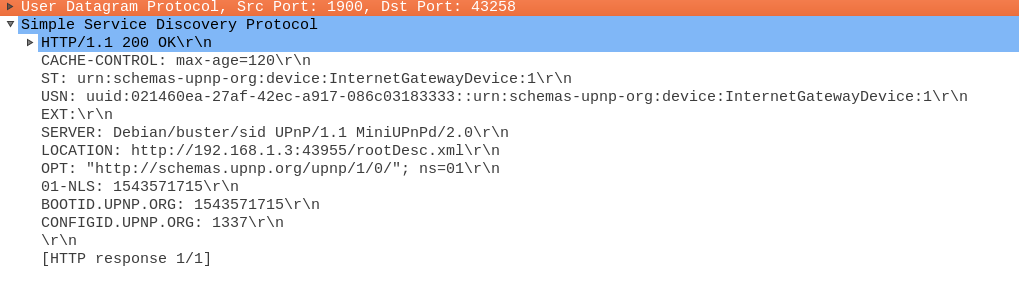
Figure 2: SSDP unicast response message
An attacker can use the URI in the “LOCATION” parameter to send an HTTP GET request and gather information about a device, which can affect the security of a network. The following figures show an excerpt of the HTTP Response to an HTTP GET query sent to the “LOCATOIN” URI. In the case of this device, the “ctl/IPConn” URL can be used to add new NAT rules on the device.

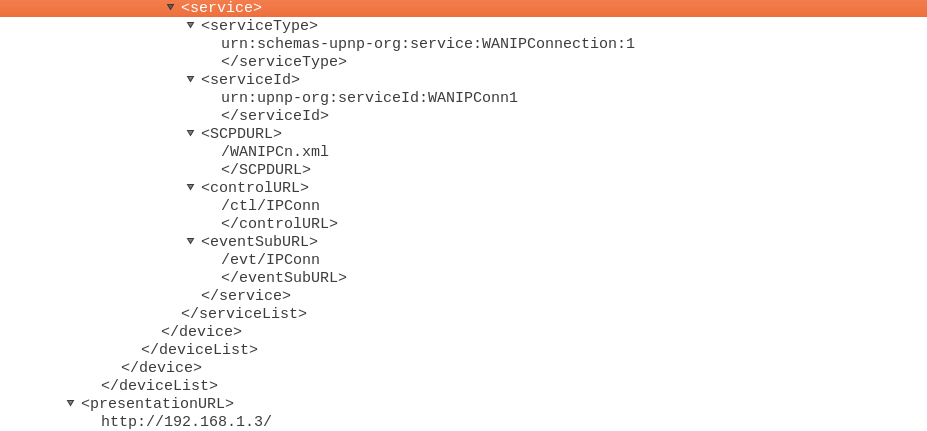
Figure 3: HTTP response to the query sent to the “LOCATION” URI
Private IP addresses are not routable or accessible across the Internet. Network devices, like routers, can isolate an organization’s internal network from the Internet. In scenarios like these, the internal network won’t be directly accessible from the Internet. However, if the edge router runs UPnP, and if it is misconfigured, an attacker can send SSDP requests to the interface connected to the Internet, and in turn, send configuration commands to the interface. It has been reported [1] that attackers can use UPnP to have NAT rules setup on the external interface of an edge device that redirects incoming traffic on that interface to TCP port 445, or any optional port, on internal hosts. This exposes machines on the internal network that were previously inaccessible. Exposing port 445 opens up machines on the internal network to a wide variety of SMB attacks, including the infamous EternalBlue exploit, and malware’s that employ these exploits. Figure 4 show a UPnP configuration request sent to a device that causes a NAT rule to be setup that forwards traffic arriving on the external interface to an internal host.


Figure 4: UPnP AddPortMapping request to UPnP enable device
UPnP NAT Rule Injection Prevention
As a security best practice, it is advisable to disable UPnP on a device where it’s not needed, and in the event the service is needed, limit its exposure to internal networks. With UDP port number 1900, used by UPnP, opening on an Internet-facing interface will enable an attacker to access internal networks via injected NAT rules as shown in this blog. Versa VOS™ (formerly FlexVNF) does not have UPnP service running, and therefore, is not affected by this UPnP vulnerability. In addition, the IPS engine in Versa VOS™ (formerly FlexVNF) can detect attempts at NAT rule injection done over UPnP.
References
[1] https://www.zdnet.com/article/hackers-are-opening-smb-ports-on-routers-so-they-can-infect-pcs-with-nsa-malware/











