What is SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)?
In an era where businesses are constantly adapting their IT infrastructures to address changing demands and evolving threats, understanding the nuances of SD-WAN is essential. This innovative technology is revolutionizing how enterprises approach network management, offering unmatched flexibility and efficiency. But what is SD-WAN, and how does it redefine traditional networking paradigms?
As we unpack the core principles of SD-WAN, let’s clarify a fundamental question: what does SD-WAN stand for, and why is it a game-changer in today’s dynamic digital environment?
Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) is a transformative technology that simplifies IT infrastructure control and management by delivering a virtual WAN architecture that securely connects users to their applications.
The hallmarks of SD-WAN are simplified branch office connectivity, increased reliability, optimized application performance, and increased network agility. One of the top SD-WAN benefits is that it enables organizations to improve network security while lowering their total costs, providing more resource usage and a more automated branch and WAN architecture that is required to fulfill modern IT business initiatives.
Businesses can also simplify their network architecture by deploying SD-WAN, meaning they’re able to easily aggregate diverse network circuits, like broadband, DIA, and LTE. These circuits can be added to existing MPLS to create a hybrid network, or they can be an alternative to MPLS using all-Internet wired and wireless connections.
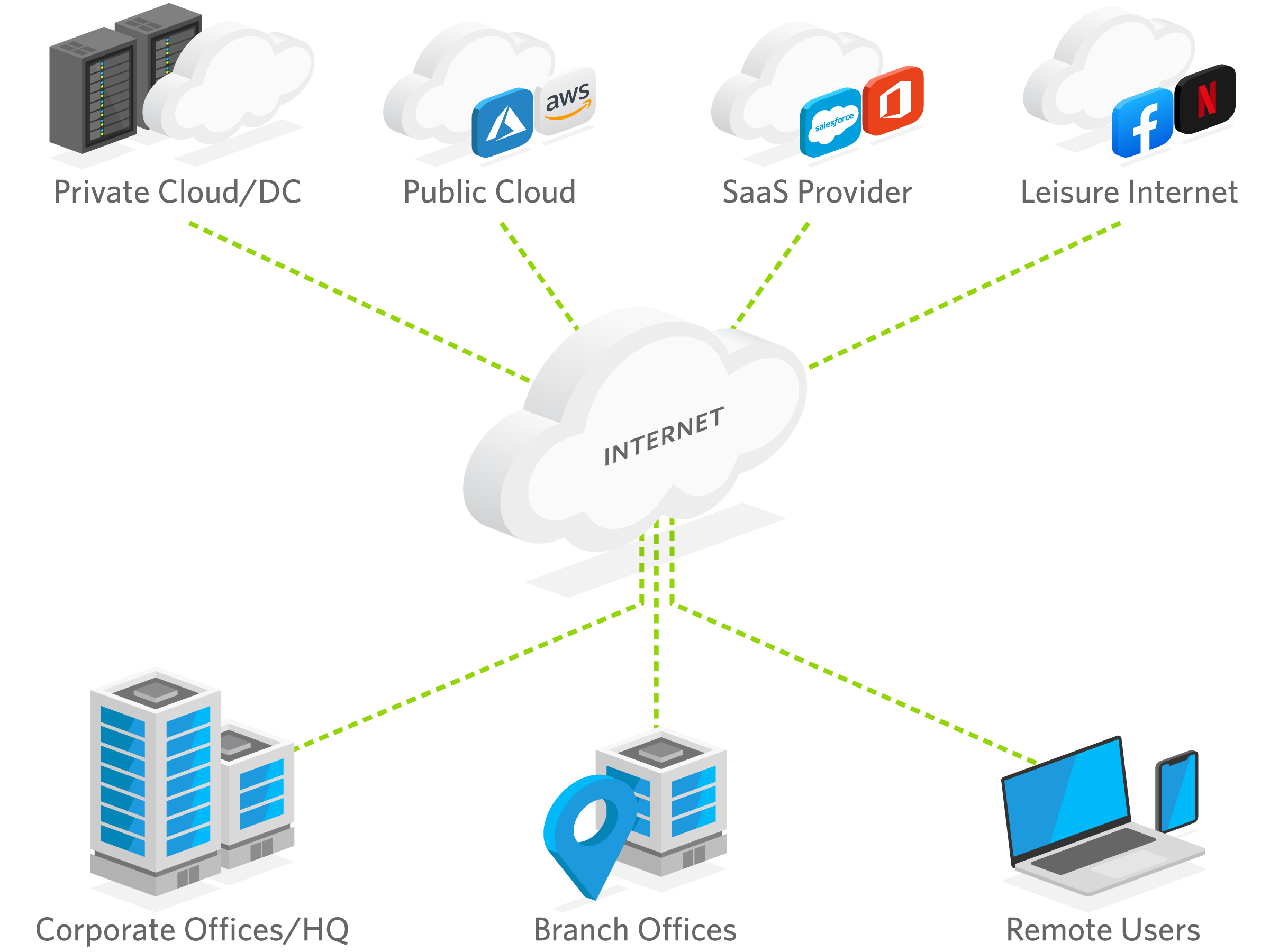
How Does SD-WAN Work: SD-WAN Explained
SD-WAN creates an overlay to virtualize the WAN with centralized control to simplify the management and deployment of branch-office services.
Overlay Network
SD-WAN creates a WAN transport agnostic overlay network and can replace legacy branch office routers simplifying the WAN infrastructure. SD-WAN provides greater control and management, providing application-layer control of application service policies, to ensure optimum application performance.
Application Awareness
A key element of SD-WAN is application-awareness. SD-WAN understands individual applications and their SLA requirements and translates them into policies that the network must adhere to. This provides active network and application experience monitoring that ensures optimal traffic delivery and QoE – whether on-premises, private/public cloud, or SaaS.
Policy-based Framework
SD-WAN also provides an automated policy-based framework that is propagated from unified control and management, all from a single-pane-of-glass interface. Visibility is enhanced, allowing better IT insights into applications, devices, users, and networking, to ensure adherence to their business goals and objectives. This simplifies ITs ability to define, control, and change business requirements across their branches, data centers, and cloud/SaaS.
Why SD-WAN?
SD-WAN solutions often offer the following:
- Lower circuit costs by using broadband, DIA, LTE
- Increase network agility by simplifying control of the entire WAN
- Create an active-active hybrid network with MPLS, broadband, DIA, LTE for increased bandwidth capacity and more efficient and higher per-site resiliency/availability
- Automate operations, while templates simplify IT workflows
- Eliminate branch office device sprawl and complexity
- Provide reliable and secure Internet access to cloud and SaaS applications
- Deliver network circuit and carrier independence
- Centralize and unify the entire WAN for simplified management, deployment, and change control
Rather than spending time and resources tediously by configuring and managing networks, an effective SD-WAN solution allows enterprises to focus on deploying applications, like IoT, VoIP, unified communications, and edge computing services.
Focusing on improving these business-oriented services, rather than managing WAN complexities, IT can add these (OTT) services to automated and programmable cloud-native platforms. Secure SD-WAN is a cloud-native platform that provides IT with an automated policy-driven, virtual WAN infrastructure. This transforms the network from a bottle-neck impediment to a business service implementation engine.

What is Secure SD-WAN? How is Versa Different?
(4:51 min)
Secure SD-WAN is a transformative technology that simplifies IT infrastructure control and management by delivering a virtual WAN architecture that securely connects users to their applications.

Versa Networks SD-WAN and Security Demo
(10:08 min)
A comprehensive demonstration providing you with the basics of Versa terminology, device onboarding, application service templates, security, and troubleshooting.

Configuring Versa SD-WAN and Microsoft Azure vWAN
(5:18 min)
Quick video to show how easy and intuitive it is to configure connectivity for Microsoft Azure vWAN and Versa Secure SD-WAN branch sites.
What are the Benefits of Secure SD-WAN?
Secure SD-WAN adds features that provide a self-healing architecture all while natively inserting network and security functions into the WAN. Secure SD-WAN accomplishes this by being application user-experience driven, monitoring the applications and network, and improving and increasing the SD-WAN security posture with an integrated platform.
Driven by application-based policies, the WAN and branch dynamically adapt to ensure network uptime, application reliability, and optimal user experience all while protecting the organization from threats and vulnerabilities.
Benefits and advantages specific to Versa Secure SD-WAN:
Secure multi-cloud connectivity that supports cloud-to-cloud, branch to multi-cloud, and business to multi-cloud
Secure multi-cloud connectivity that supports cloud-to-cloud, branch to multi-cloud, and business to multi-cloud
Embedded and robust next-generation security features such as Universal Threat Management and Role-Based Access Control
Full multi-tenancy for micro-segmentation of line of business, tenant, and control, with unique policies per segment
Micro-segmentation across the entire network to reduce risk zones and lateral movement
Context-based network and security policies, and traffic steering, based on users, devices, locations, and applications
How SD-WAN Solves Modern IT Network Challenges
Cloud, virtualization, mobility, IoT, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning are all contributing massive amounts of traffic and data over enterprise WANs. Unfortunately, they are also creating network reliability and performance challenges and causing security breaches by exponentially expanding the attack surface.
These technologies have created the need for a simplified and consolidated IT infrastructure. Robust cloud-native VNF-based network and security services are needed in the service provider core, or central enterprise IT infrastructure, and within the network edges.
CSecure SD-WAN technology enables flexibility to be deployed as the uCPE platform to host other services, or as a VNF on a third-party uCPE or virtualization platform. Secure SD-WAN has the routing, SD-WAN, analytics, security, and more, all within a single software platform.
This SD-WAN solution provides a cohesive, virtualized network, and a multi-layered security approach that eliminates siloed, single-function appliances that add unnecessary risk, complexity, and cost.
SD-WAN Meets Business Objectives
Legacy WAN as Bottleneck
Any multi-location or digital-first organization that uses the WAN to communicate and connect with employees, customers, and partners, should have the business objectives directly influencing its entire WAN fabric. Yet, enterprise WANs, for the most part, unintentionally hinder their business goals. A legacy WAN becomes the bottleneck for the business operations because of an archaic approach to policy creation, adherence, and execution.
Business Intent Drives SD-WAN
With an SD-WAN network, business intent and application experience drive the underlying policy architecture, automates the deployment, and creates a dynamic environment that can quickly adhere and execute on the business objectives.
So, how does an enterprise SD-WAN solution adhere to become driven by business intent quickly and dynamically? Two key components are required to accomplish this; a business-aware architecture, and a simplified and consolidated platform.
Secure SD-WAN addresses network challenges by providing a secure cloud IP platform that simplifies management and administration. Secure SD-WAN brings business goals and intent into the WAN through our business-aware architecture. Secure SD-WAN simplifies network and security infrastructure with a multi-purpose platform with native networking and security apps and services capabilities.
Secure SD-WAN removes the complexity of maintaining uniform policies by ensuring that all policies are up-to-date and fit their objectives across all disparate platforms:
- Secure SD-WAN’s identity management ensures protection of credentials and therefore access control by binding contextual policies with users, applications, destinations, and paths, through an Active Directory integration.
- Secure SD-WAN includes advanced layers 3-7, with full routing, SD-WAN, and a next-generation security stack
- Everything is managed by an SD-WAN Director with orchestration and analytics, and all functionality is incorporated into a single view which is easy to configure and control the entire SD-WAN and WAN edge security
SD-WAN vs. SDN
SD-WAN is different from SDN because it is used for connecting geographically distributed locations, sites, and remote users while an SDN is used for managing Local Area Networks (LAN) or carrier’s core networks.
Because SDN is primarily used in traditional data centers, SDN enables services on-demand, reducing the high operational costs all while improving the network performance. SD-WAN differs by being a cost-effective alternative to the traditional Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) networks by providing scalable and secure connectivity anywhere in the world. Essentially, SD-WAN performs SDN functions but for the Wide Area Network (WAN).
Both SDN and SD-WAN serve a similar purpose and are based on the same architecture of separating the control and data forwarding planes. Both SDN and SD-WAN can be virtualized to implement additional Virtual Network Functions (VNF) such as firewall and unified threat management functionality as well as WAN optimization.
Here is a breakdown of the two technologies:
SDN |
SD-WAN |
|---|---|
| Used for on-premises data centers and service provider infrastructure | Used for branch sites and remote users as well as data centers |
| Configured by a user or administrator | Configured and managed by the vendor |
| Delivers high-bandwidth on-demand | Delivers secure access and intelligent traffic prioritization |
| Provides a centralized console for orchestration and control | Provides a centralized console for orchestration, control, and zero-touch provisioning |
| Underpins core network infrastructure | Underpins existing Virtual Private Networks (VPN) |
| Leverages a variety of commodity and specialized switching hardware | Leverages off-the-shelf x86 appliances – physical, virtual, cloud |
| Reduces OpEx Costs | Reduces both OpEx and CapEx costs |
SD-WAN vs. MPLS
The major distinction between SD-WAN and MPLS is that SD-WAN is a virtualized infrastructure and MPLS is hardware-based. SD-WAN is often times considered the software abstraction of MPLS technology that brings secure, private connection to branch sites and remote users. MPLS is more expensive, dedicated to a specific organization, and handles failover with backup links. SD-WAN, on the other hand, is more cost efficient by handling multiple types of network connections and handles failover with real-time traffic steering and intelligence.
Both SD-WAN and MPLS offer network performance, quality, and availability to data centers and branch offices. SD-WAN often manages MPLS connections along with other types such as broadband, long-term evolution (LTE), and route traffic over the best available path in real-time. Both options offer reliable, secure, and private connections but differ greatly in flexibility, costs, and capabilities.
Here is a breakdown of the two technologies:
MPLS |
SD-WAN |
|---|---|
| Traffic is backhauled to the datacenter | Used for branch sites and remote users as well as data centers |
| Dedicated private network with limited but reliable bandwidth | Multiple transport media are available: DIA, Broadband, LTE, MPLS, and more |
| Data partition but no encryption | Encrypted VPN tunnels |
| Higher costs due to predetermined paths and hardware | Lower costs due to traffic steering and software |
| User experience and application performance is affected by traffic volume | User experience and application performance is not affected by traffic volume |
| No built-in security | Integrated security stack |
| Manual configuration and no application visibility | Real-time automation and analytics for visibility |
How To Deploy SD-WAN
Network architectures have always found ways to adapt to changing business dynamics to address modern requirements. Legacy WANs are no longer adequate to meet business needs and most organizations are deploying a hybrid WAN architecture. Hybrid WANs benefited from adopting a software-defined approach, which led to the automation, agility, and increased intelligence from SD-WAN architecture.
Today, SD-WAN has gained greater value through being delivered and managed from the cloud: allowing better speed, scalability, and flexibility. Cloud-delivered SD-WAN is a powerful automated, on-demand, and proactive business approach that enterprises leverage to streamline secure connectivity services that can greatly optimize branch offices and IoT.
SD-WAN devices are better at understanding application traffic flows than legacy WAN. This optimization in application traffic flow allows an administrator to use application and identity-driven policies to make intelligent decisions that adhere to business goals and objectives.
For example: to ensure voice service is always optimal, an administrator can analyze voice traffic to determine how well the user experience is or analyze network circuits to determine how well they are performing. Then, the administrator can correlate those together to make dynamic decisions that optimally traffic steer across the WAN. Application and identity-driven policies can be contextual to who you are, what you are using, and where you are.
Secure SD-WAN for Every Enterprise
Secure SD-WAN ensures application security, reliability, and performance for every industry, vertical, and use cases such as enabling healthcare records, banking systems, retail POS systems, airline reservations, transportation logistics, and much more. Whether the application is for internal business operations, commerce, customer relationship management, industrial and utility systems – everything today is network connected and can be enhanced by SD-WAN.
Secure SD-WAN frees IT from single-function and proprietary hardware, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware for each network function. Virtual network services can be provisioned on a universal CPE (uCPE), using an x86-based appliance that hosts Secure SD-WAN’s software and supports 3rd-party VNFs.
Enterprises can take advantage of a software-only solution, that gives them the cost and operational flexibility, and ensures they have the control to deliver on their business objectives. Furthermore, organizations can leverage an open-standard-based cloud-native, multi-stack solution for embedded and robust network and security capabilities that optimize application performance all while increasing security hygiene. Secure SD-Wan needs to integrate with existing brownfield networks at the underlay level while providing a migration to complete Software-Defined networking on-premises and in the cloud. By doing so, enterprises can meet the demands of a modern IT landscape.
SD-WAN FAQs
What is the difference between WAN and SD-WAN?
Unlike traditional WAN, SD-WAN is software-defined and comes with several advantages. First, it allows for the elimination of costly MPLS circuits. SD-WAN also enlists local internet offloading and helps get user traffic closer to cloud services.
It provides real-time traffic monitoring as well and is able to support high-bandwidth intensive applications, which can be a challenge for traditional WAN infrastructures.
Is SD-WAN a router?
No. The SD-WAN model effectively replaces a router. Traditional WANs based on conventional routers are not designed for the cloud. SD-WANs, on the other hand, fully support applications hosted in on-premise data centers, public or private clouds, and SaaS services.
Is SD-WAN a VPN?
No. VPNs send all traffic over a single network link. SD-WANs route traffic over multiple transport media. For enterprises that require scalability, high performance, reliability, and agility, SD-WAN is far preferred over a VPN.
Learn More
Find more research, analysis, and information on SASE (Secure Access Service Edge), networking, security, SD-WAN, and cloud from industry thought leaders, analysts, and experts.
Versa Secure SD-WAN – Simple, Secure, and Reliable Branch to Multi-Cloud Connectivity
Versa Secure SD-WAN is a single software platform that offers multi-layered security and enables multi-cloud connectivity for Enterprises.
Accelerating Digital Transformation with
Senior executives from Versa Networks and First Data Corp. (now Fiserv) outline two distinct journeys of successfully deploying the optimal solution for the new WAN and the key criteria for qualifying Secure SD-WAN in support of digital transformation strategies.
